Redirecting in 10 seconds...
Click here for Pituitary gland
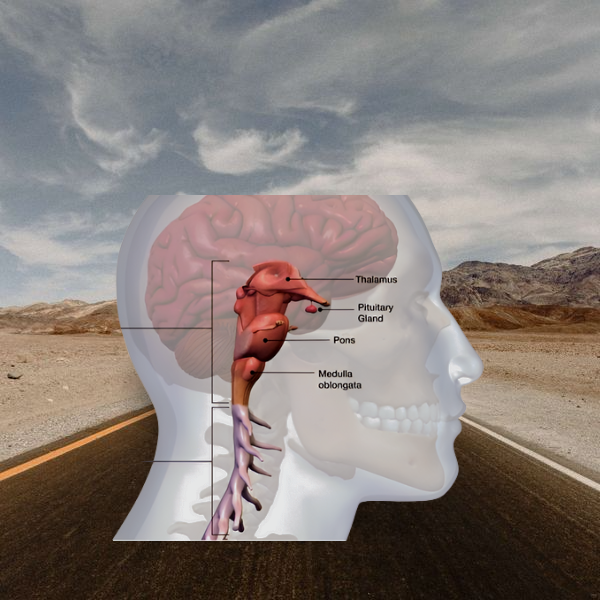
Pituitary gland
Pituitary gland:
§
It is the brain that determines every
action of the body.
§
Pituitary gland is responsible for
all the functions of height, growth of the reproductive system.
§
The Pituitary gland is the master
gland. This gland is located in the brain, below the hypothalamus gland, about
the size of a small pea. It sits in its own little chamber under the brain
known as the sella turcica.
§ It
is important in endocrine glands and weighing on average, 0.5 grams in humans. This, small pea-sized gland can be divided into three parts namely
anterior lobe, intermediate lobe and posterior lobe.
§
The hypothalamus controls both the
nervous system and the endocrine system. The hypothalamus controls the
secretion of eight major hormones secreted by the pituitary gland.
§
Pituitary gland is responsible for
keeping the body temperature under control, taking the necessary amount of
water and food for the body. This gland is also responsible for our sexual
activities, growth of organs and many more.
§
It is the hormones secreted from here
that stimulate other endocrine glands in the body and determine the function of
the body.
§
Arterial supply of the Pituitary gland:
v
Superior hypophyseal artery
v
Infundibular artery
v
Prechiasmal artery
v
Inferior hypophyseal artery
v
Capsular artery
v
Artery of the inferior cavernous
sinus.
§
Hormones of the Pituitary gland:
Anterior lobe:
§
From the anterior lobe of the
Pituitary gland, the hormones that stimulate the growth of the body and the
growth of the reproductive system are secreted. Human growth hormone, follicle
stimulating hormone etc. are important in this.
§
Follicle-stimulating hormone is very
important for the development of male and female reproductive organs such as
testicles and vulva and uterus.
§
Similarly, thyroid stimulating
hormone and adrenal stimulating hormones are secreted here.
§
This is also where prolactin, the
hormone that stimulates milk secretion after childbirth, is secreted.
§
The gland that secretes melanin in
our skin is melanocytes gland. Melanocytes gland is stimulated and controlled
by the pituitary gland.
v Growth
hormone:
·
In children, growth hormone
stimulates growth. In other words, it helps children grow taller.
·
In adults, growth hormone helps
maintain healthy muscles and bones and impacts fat distribution.
·
GH deficiency: Pituitary doesn’t release enough growth hormone causes a lack of growth and
development and delayed puberty in children. In adults, it causes metabolic
issues.
v Thyroid
stimulating hormone:
·
TSH stimulates thyroid to produce
thyroid hormones that manage the metabolism, energy levels and the nervous
system.
·
Hypothyroidism happens
when pituitary doesn’t release enough thyroid
stimulating hormone. It causes low thyroid hormone levels.
v Adreno-corticotrophin
hormone:
·
ACTH plays a role in how your body
responds to stress.
·
It stimulates the adrenal glands to
produce cortisol, which has many functions, including regulating metabolism,
maintaining blood pressure, regulating blood sugar levels and reducing inflammation,
among others.
·
Central adrenal insufficiency happens when
pituitary doesn’t release enough ACTH. This causes the body to be unable to
release cortisol.
v Follicle-stimulating
hormone:
·
FSH stimulates sperm production in
people assigned male at birth.
·
Follicle stimulating hormone stimulates the
ovaries to produce estrogen and plays a role in egg development in people
assigned female at birth.
v Melanocyte
stimulating hormone
v
Luteinizing hormone:
·
LH stimulates ovulation in people
assigned female at birth and production in people assigned male at birth.
·
Central hypogonadism happens when pituitary doesn’t
release enough LH
and FSH. It causes issues with sexual function and development and
fertility.
v Prolactin:
·
prolactin stimulates breast milk
production after giving birth.
v Endorphins:
·
Endorphins have pain relieving
properties and are thought to be connected to the “pleasure centers” of the
brain.
v Beta-
melanocyte stimulating hormone:
·
This hormone helps to stimulate
increased pigmentation of the skin in response to exposure to ultraviolet
radiation.
Posterior lobe:
§ Antidiuretic hormone:
·
This is also called Vasopressin.
·
It is secreted in the posterior lobe
of Pituitary gland, which monitors the amount of water in our body, stimulates
the kidneys to excrete excess water, and prevents the body’s water from being
completely released.
§ Oxytocin:
·
Similarly, the hormone oxytocin,
which is very important for women, is secreted here.
·
It is an important hormone that helps
women during labor to dilate the birth canal, induce labor, contract the uterus
after delivery, prevent bleeding, stimulate milk secretion, and increase
mother-child bonding.
·
Hypothalamus makes oxytocin, and
pituitary gland stores and releases it.
·
In people assigned male at birth,
oxytocin plays a role in moving sperm.
Symptoms of damaged Pituitary gland:
§
Headaches.
§
Unexplained weight gain.
§
Feeling dizzy and nauseous.
§
Muscle wasting.
§
Loss of libido.
§
Pale complexion.
§
Coarsening of facial features.
§
Vision problems.
Prevalence and detection method:
§
Pituitary gland can be affected due
to various reasons including brain tumor, tumor in pituitary gland, accident.
As a brain tumor compresses the pituitary gland, its function is completely
changed.
§
As a result, the pituitary gland
becomes inflamed, hormone secretion may decrease or increase. Whatever happens
in this can have a major impact on the body.
§
This impact can be detected through a
simple blood test that measures the level of hormones in the blood.
§
The doctor will decide which hormone
to measure depending on the type of the patient’s condition.
§
After that doctors will determine
whether the pituitary gland is shrunk or enlarged through a CT or MRI scan and
decide what kind of treatment to give.




No comments:
Post a Comment